Enhancing Kubernetes Configuration with Intelligent YAML Editing
3 min read
As an administrator managing multiple Kubernetes clusters, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your configurations is paramount. Mistakes in YAML files, even minor ones, can have catastrophic effects on your infrastructure and business continuity. This blog post explores how leveraging advanced YAML editing tools can significantly enhance your workflow, providing safety checks and autocompletion to help you configure your clusters more rapidly and with greater confidence.
User Story
As an administrator of multiple Kubernetes clusters, my tools for editing YAML should leverage knowledge of YAML syntax and schemas to provide additional safety checks and autocompletion so that I can configure my cluster more rapidly and confidently.
Solution: Integrating YAML Language Server
To address these needs, we propose integrating the YAML language server (yaml-language-server) into your development environment. This tool, coupled with Kubernetes and Flux configurations, enhances the editing experience by ensuring syntax correctness and schema compliance.
Background
Kubernetes: A Unified Infrastructure API
Kubernetes abstracts infrastructure management across various clouds and on-premises environments, providing a uniform API. This abstraction simplifies the deployment and management of applications at scale.
Flux: GitOps for Kubernetes
Flux (fluxcd.io) revolutionizes Kubernetes management with GitOps practices. It enables declarative management of your Kubernetes infrastructure, allowing you to deploy directly from a Git repository. This approach ensures consistency and simplifies the deployment pipeline.
Detailed Description
Setting Up the YAML Language Server
-
Install the YAML Language Server
Begin by installing the YAML language server in your development environment. Since I am currently using NvChad, I first configure mason to ensure the language server is installed by adding the following to
lua/plugins/init.lua:{ "williamboman/mason.nvim", opts = { ensure_installed = { ... "yaml-language-server", }, }, }, -
Configure the Editor
Enable the LSP (Language Server Protocol) for Kubernetes in your editor. This setup will provide features like syntax validation, schema validation, and autocompletion.
For Neovim users, we can configure nvim-lspconfig to use the language server by adding the following to
lua/configs/lspconfig.lua:lspconfig.yamlls.setup { settings = { yaml = { schemas = { kubernetes = "/*.yaml" } } } }The
yaml.schemas.kubernetessetting sets a schema association to try and parse YAML files with Kubernetes schemas.
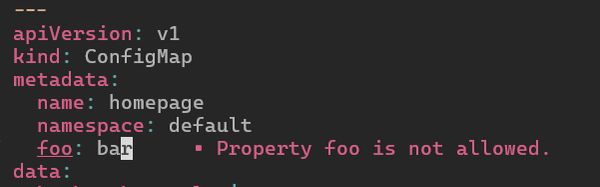
Example: Testing Validation of a ConfigMap
To illustrate the benefits, let’s walk through an example of validating a ConfigMap:
-
Step 1: Create a Sample ConfigMap YAML File
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: example-config data: key: value -
Step 2: Enable LSP and Validate
With the YAML language server configured, your editor will highlight syntax errors and schema violations. This feature ensures that your ConfigMap adheres to the correct structure and data types.
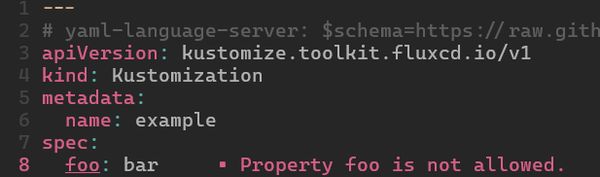
Inline Schemas for Flux
Flux configurations can also benefit from inline schemas. Let’s look at how you can validate a Flux Kustomization fileusing an inline schema association:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datreeio/CRDs-catalog/main/kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/kustomization_v1.json
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: example
spec:
key: value
The YAML language server will now validate the Kustomization file against the specified schema, ensuring that all resources are correctly defined.
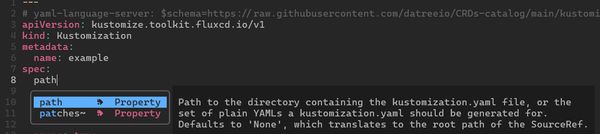
Schema-Aware Autocomplete
One of the standout features of the YAML language server is its schema-aware autocomplete functionality. This feature significantly speeds up the configuration process by suggesting valid options based on the schema.
-
Example Usage
As you type, the editor will provide suggestions that are contextually relevant, reducing the chance of errors and enhancing productivity.
Conclusion
In environments where even a small change in configuration can disrupt service for all customers, intelligent safety checks become indispensable. The YAML language server not only validates syntax but also ensures schema conformance, catching errors before they are deployed.
By leveraging the LSP abstraction, any supported editor can benefit from these features, making your Kubernetes configuration process safer, faster, and more reliable. Embracing these tools can be a game-changer, allowing administrators to manage complex Kubernetes environments with ease and confidence.